Overview
This documentation covers most of advanced Plumier functionalities. By reading this documentation you will be able to extends the framework functionalities to give plumier a new ability.
caution
By reading this documentation assume that you are already familiar with basic Plumier functionalities such as parameter binding, routing, type conversion etc.
Plumier has some built-in functionalities such as validators, parameter binders, authorizer etc. If those functionalities doesn't fit your needs, you can extends Plumier capability by providing your own custom extension. Plumier provided some interfaces contract to easily extend its capability.
There are some knowledge base you need to know to make a better understanding on how things work inside the framework before start creating custom extension.
Plumier Middleware in a Nutshell#
The term of middleware in Plumier is the same as in other framework such as Express and Koa. All functionalities (validator, authorization, parameter binding etc) in Plumier are implementation of middleware.
Unlike Express, Plumier middleware used a modern pipeline. Instead of using a chain of callback Plumier middleware used chain of promise (async/await) executed from one to another waiting the execution result of the next middleware.
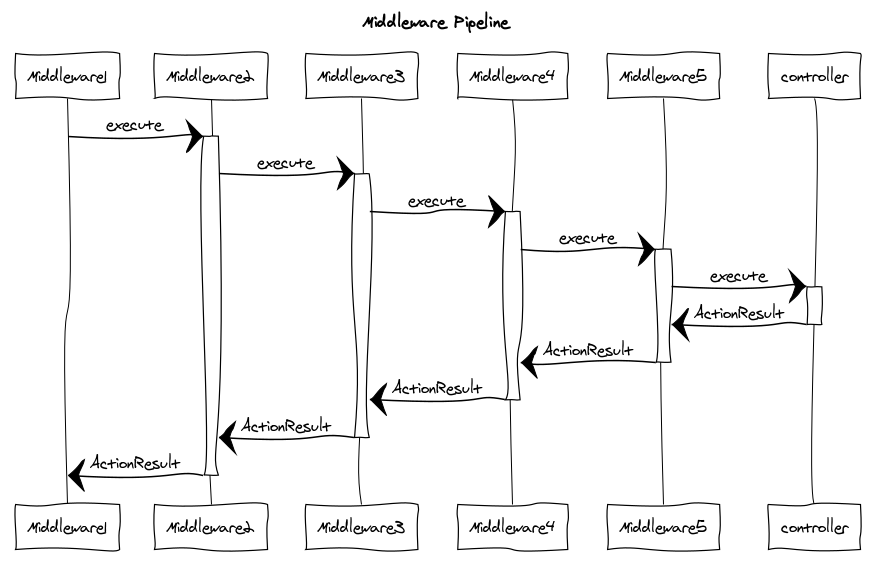
This pipeline has better execution control than Express, because the previous middleware free to await the next middleware execution or return a new ActionResult immediately and stop the execution pipeline without touching the controller.
This behavior very important for some functionalities such as Validation and Authorization where middleware can stop the pipeline execution immediately when some state doesn't match the preferred condition and returned error message immediately.
This behavior also has better error handling because API programmer free to throw error anywhere inside middlewares or controllers because its guaranteed will be caught by the higher middleware.
Simplest custom middleware example is like below
Above code showing a simplest custom middleware it does nothing except execute the next middleware and pass the result into the higher middleware.
Above code is another version of middleware, its created using functional custom middleware, it has the same behavior with the previous example.
Invocation is an object represent the next process will be invoked by the middleware. It has proceed() method used to execute the next process and returned the execution result Promise<ActionResult>. Invocation has ctx property which is the Context useful to get current request information.
Context#
Context in Plumier (usually the variable named ctx) is derived from Koa context, it encapsulate HttpRequest and HttpResponse object into a single object, it mostly used in every custom extension.
Context can be accessed from inside controller using parameter binding @bind.ctx() or from inside any custom extension. Even though Context has tons of properties, usually only a few will be used, here are list of most used properties:
ctx.request.bodythe request body. Don't confuse withctx.bodybecause its the response body.ctx.queryorctx.request.querythe request query case insensitive. Can be access usingctx.query.myQuery,ctx.query.MYQUERY,ctx.query["myquery"]orctx.query["MYQUERY"]ctx.headerorctx.request.headerthe request header.ctx.cookiesthe cookiectx.state.userthe current login user (JWT claim)ctx.userthe current login user (same asctx.state.user)ctx.configthe Plumier application configurationctx.routesarray of all route information used by the route generator.ctx.routethe current route information, contains metadata information of current controller or action handles the request. For request doesn't associated with controller the value will beundefined.ctx.parametersarray of value that will be bound to controller's method. The value arranged in a correct order match with methods parameter. This property only available on controller/method middleware
For a complete reference about Context and its properties can be found in Koa documentation.
Application Lifecycle#
When an Http Request issued into Plumier application, the process goes through a series of processing steps categorized into three main process like picture below.
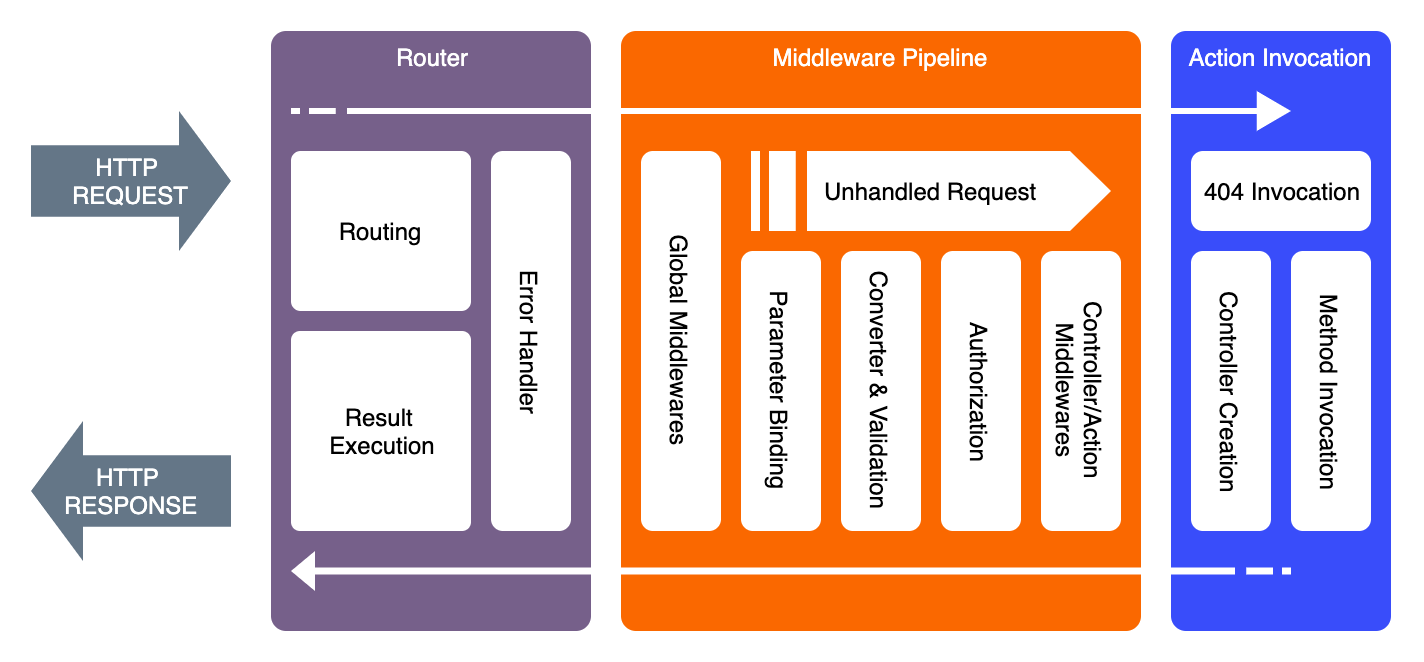
The execution process start from the left to right to pass the request that will be processed by controller and then returned back from right to left for the controller execution result that will be rendered into http response.
All the child process of the Middleware Pipeline is extensible by using custom extension with specific registration:
- Custom global middleware middleware registered using Plumier application during the application bootstrap using
app.use()method. - Custom parameter binding registered on the appropriate parameter using
@bind.custom()decorator. - Custom validator registered on the appropriate parameter or domain model property using
@val.custom()decorator. - Custom authorization registered on appropriate controller, methods, parameter or domain model properties on deep nested property using
@authorize.custom()decorator. - Controller/method middleware register on controller or method using
@middleware.use()decorator.
Note that the execution order of the child process of the middleware pipeline is important. The execution start from left to right so global middleware has more control than the other process.
The execution order also affect the ctx.parameters value which will only available after Parameter Binding process, so global middleware will not be able to access them.
Metaprogramming#
One of Plumier key feature is it provide metadata information for metaprogramming. This metadata information accessible from all custom extensions.
Request metadata is specialized class contains metadata of current request such as controller, action and action parameter useful for metaprogramming. It contains some properties:
actionParamscurrent action parameters metadata, used to access parameter value, name etc.controllercurrent controller object graph, contains information about controller name, decorators, methods, constructor etc.actioncurrent action object graph, contains information about action name, parameters, decorators etc.currentmetadata information where the appropriate decorator applied, can be Class metadata, Method metadata, Property metadata or Parameter metadata. For global middleware thecurrentproperty will beundefined.
This request metadata usually accessible from metadata property from Invocation class, ValidatorContext class, and AuthorizerContext class.
Custom Middleware#
There are two kind custom middlewares: Global middleware and Controller/method middleware. Technically both are the same but there are some distinction between them:
ctx.routeaccessible in both, but in global middleware the value is optional (can beundefined), because global middleware kept executed even the request doesn't has appropriate controller.ctx.parameterswith cleansed value (converted/validated) only accessible from controller/method middleware- Controller/method middleware will never touched when there are validation error or authorization error occur.
- Global middleware derived from
CustomMiddlewareorCustomMiddlewareFunction. Controller/action middleware derived fromCustomMiddleware<ActionContext>orCustomMiddlewareFunction<ActionContext>.
Example Global Middleware#
Global middleware always executed on every request, this behavior can be used to create a virtual endpoint without having a controller that handle the request. For example we create the /hello-world endpoint and returned a JSON.
Register the middleware from the Plumier application like below
Above code will handle the /hello-world then return an ActionResult immediately if the path match the criteria else the next invocation executed.
Example Controller/Method Middleware#
Controller/Method middleware has access to the ctx.route and ctx.parameters. This property best used for programming. On this example will will create a logging middleware to print the controller name, method name, the parameters applied and the time used to complete the request.
Register the middleware on top of Controller
Above code showing that the middleware applied on the controller, its mean it will log the controller name, method name etc when all the three endpoints (GET /animals/:id POST /animals PUT /animals/:id) accessed.
Custom Parameter Binding#
Custom parameter binding extends the parameter binding functionalities, signature of custom parameter binding is like below
Custom parameter binder receive single parameter which of type Context and return the value that will be bound to the parameter.
Above code will bind the auth parameter with the Authorization header.
Custom Validator#
Custom validator extends Plumier validator functionalities. For example we want to create adult age restriction validation, the implementation simply like below
Custom validator can be applied on controller's method parameter or on domain property.
Above code will restrict access to the GET /picture/adult endpoint by validating the age property of the current login user provided by the JWT token claim.
Refer to the custom validator documentation for more info.
Custom Authorization#
Custom authorization extends Plumier authorization functionalities. This custom extension useful when you want to secure an endpoint based on specific data.
For example an online marketplace user free to create their own shop and assigned as the ShopAdmin by default, further more they can assign another user as Staff.
Above logic is impossible when implemented using default Plumier authorization because user role is dynamic based on data. Here are example of the Shop controller.
The expected endpoint access is like below:
| Endpoint | Authorize | Description |
|---|---|---|
POST /shops | Authenticated | All login user can create new shop |
GET /shops/:shopId | Public | All user login or non login can show |
PUT /shops/:shopId | ShopAdmin, Staff | Only Admin and Staff of the shop (shopId) can modify |
DELETE /shops/:shopId | ShopAdmin | Only Shop Admin can delete the shop |
Implementation of the custom authorizer is like below:
Above code showing that we create a custom authorizer by directly returned the @authorize.custom(), its mean the shopUser function is a custom decorator that can be applied on controller or method.
Above authorizer reads the metadata information of current request to check wether the method has parameter named shopId and extract the shopId value from the metadata.actionParams. By using this trick this decorator can be reuse in any method has parameter named shopId.
Custom authorizer above can be applied easily on the previous controller.
Code above showing that we applied our custom authorizer above modify and delete method. Note that both method has shopId parameter.
By applying authorizer above modify method (PUT /shops/:shopId) only accessible by ShopAdmin and Staff other users will not has access to the method. So does the delete method only accessible by ShopAdmin.
